dubbo源码研究之config模块
dubbo模块说明
- dubbo-common 公共逻辑模块,包括Util类和通用模型
- dubbo-remoting 远程通讯模块,相当于Dubbo协议的实现,如果RPC用RMI协议则不需要使用此包。
- dubbo-rpc 远程调用模块,抽象各种协议,以及动态代理,只包含一对一的调用,不关心集群的管理
- dubbo-cluster 集群模块,将多个服务提供方伪装为一个提供方,包括:负载均衡, 容错,路由等,集群的地址列表可以是静态配置的,也可以是由注册中心下发。
- dubbo-registry 注册中心模块,基于注册中心下发地址的集群方式,以及对各种注册中心的抽象。
- dubbo-monitor 监控模块,统计服务调用次数,调用时间的,调用链跟踪的服务。
- dubbo-config 配置模块,是Dubbo对外的API,用户通过Config使用Dubbo,隐藏Dubbo所有细节。
- dubbo-container 容器模块,是一个Standlone的容器,以简单的Main加载Spring启动,因为服务通常不需要Tomcat/JBoss等Web容器的特性,没必要用Web容器去加载服务。
今天开始从dubbo入口,config模块开始研究。
config模块和Service模块是API,其他为SPI实现。
config模块uml类图
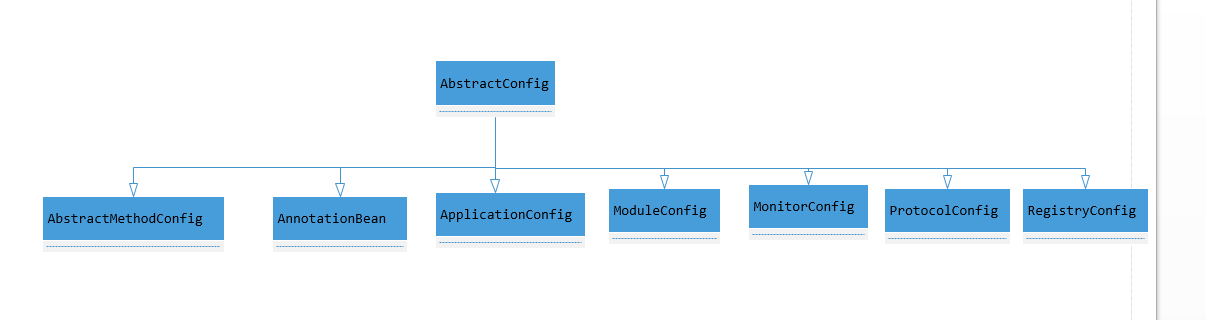
AbstractConfig类提供几个主要的方法 appendAnnotation,appendProperties,appendParameters,appendAttributes
其他子类提供相关自身的属性。
AbstractConfig类里面大量通过 反射和javabean约定获取相关值,特别注意的是toString方法注释提到的防御性容错
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(t.getMessage(), t);
return super.toString();
}
|
防御性容错在此处使用,提升代码健壮性。
AnnotationBean是子类里面一个比较特殊的类。因为该类是处于com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring包下面。
该类属于config模块的spring 扩展,支持通过注解来配置dubbo。
AnnotationBean实现了DisposableBean, BeanFactoryPostProcessor, BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware这四个接口。
DisposableBean:资源清理接口
BeanFactoryPostProcessor,BeanPostProcessor:作用类似,都是在bean创建之后的扩展接口。
ApplicationContextAware:获取spring上下文接口。
通过该类可以看出,dubbo注解实际上是spring注解的扩展,也就是说使用dubbo注解的前提是使用spring作为dubbo的容器。
@servcie暴露dubbo服务配置的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (! isMatchPackage(bean)) {
return bean;
}
Class<?> clazz = bean.getClass();
if(isProxyBean(bean)){
clazz = AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean);
}
Service service = clazz.getAnnotation(Service.class);
if (service != null) {
ServiceBean<Object> serviceConfig = new ServiceBean<Object>(service);
if (void.class.equals(service.interfaceClass())
&& "".equals(service.interfaceName())) {
if (clazz.getInterfaces().length > 0) {
serviceConfig.setInterface(clazz.getInterfaces()[0]);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to export remote service class " + clazz.getName() + ", cause: The @Service undefined interfaceClass or interfaceName, and the service class unimplemented any interfaces.");
}
}
if (applicationContext != null) {
serviceConfig.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
if (service.registry() != null && service.registry().length > 0) {
List<RegistryConfig> registryConfigs = new ArrayList<RegistryConfig>();
for (String registryId : service.registry()) {
if (registryId != null && registryId.length() > 0) {
registryConfigs.add((RegistryConfig)applicationContext.getBean(registryId, RegistryConfig.class));
}
}
serviceConfig.setRegistries(registryConfigs);
}
if (service.provider() != null && service.provider().length() > 0) {
serviceConfig.setProvider((ProviderConfig)applicationContext.getBean(service.provider(),ProviderConfig.class));
}
if (service.monitor() != null && service.monitor().length() > 0) {
serviceConfig.setMonitor((MonitorConfig)applicationContext.getBean(service.monitor(), MonitorConfig.class));
}
if (service.application() != null && service.application().length() > 0) {
serviceConfig.setApplication((ApplicationConfig)applicationContext.getBean(service.application(), ApplicationConfig.class));
}
if (service.module() != null && service.module().length() > 0) {
serviceConfig.setModule((ModuleConfig)applicationContext.getBean(service.module(), ModuleConfig.class));
}
if (service.provider() != null && service.provider().length() > 0) {
serviceConfig.setProvider((ProviderConfig)applicationContext.getBean(service.provider(), ProviderConfig.class));
} else {
}
if (service.protocol() != null && service.protocol().length > 0) {
List<ProtocolConfig> protocolConfigs = new ArrayList<ProtocolConfig>();
for (String protocolId : service.protocol()) {
if (protocolId != null && protocolId.length() > 0) {
protocolConfigs.add((ProtocolConfig)applicationContext.getBean(protocolId, ProtocolConfig.class));
}
}
serviceConfig.setProtocols(protocolConfigs);
}
try {
serviceConfig.afterPropertiesSet();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw (RuntimeException) e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
serviceConfig.setRef(bean);
serviceConfigs.add(serviceConfig);
serviceConfig.export();
}
return bean;
}
|
主要是先获取类上面的@servcie注解,然后new 一个对应的ServiceBean,ServiceBean继承于ServiceConfig,同时实现了spring bean的相关接口 InitializingBean, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener, BeanNameAware。
最后该serviceBean保存到线程安全的容器里面去。
@service解析是在 postProcessAfterInitialization里面
@Reference解析是在postProcessBeforeInitialization里面,两者的时机是不一样的。
1
2
3
4
|
String key = reference.group() + "/" + interfaceName + ":" + reference.version();
ReferenceBean<?> referenceConfig = referenceConfigs.get(key);
|
从该代码可以看出,服务接口的唯一性,由group,interfaceName 和version一起决定。
